New Customers Sepcial: Get 15% off, use the code "NEW15" at checkout. Shop Now!
3D Model Development
Tridix Bio offeres advanced 3D model development services leveraging state-of-the-art spheroid and organoid generation technologies. Our in vitro cellular models are designed to closely mimic human physiology and support disease-relevant research. These models include, but are not limited to, MASH (Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis) models derived from primary human liver cells, CNS disease models such as ALS and FTD developed from iPSC-derived neurons, as well as a wide range of tumor and stem cell spheroids. Tridix's 3D platforms provide robust and customizable tools to accelerate target validation, drug screening, and mechanistic studies.
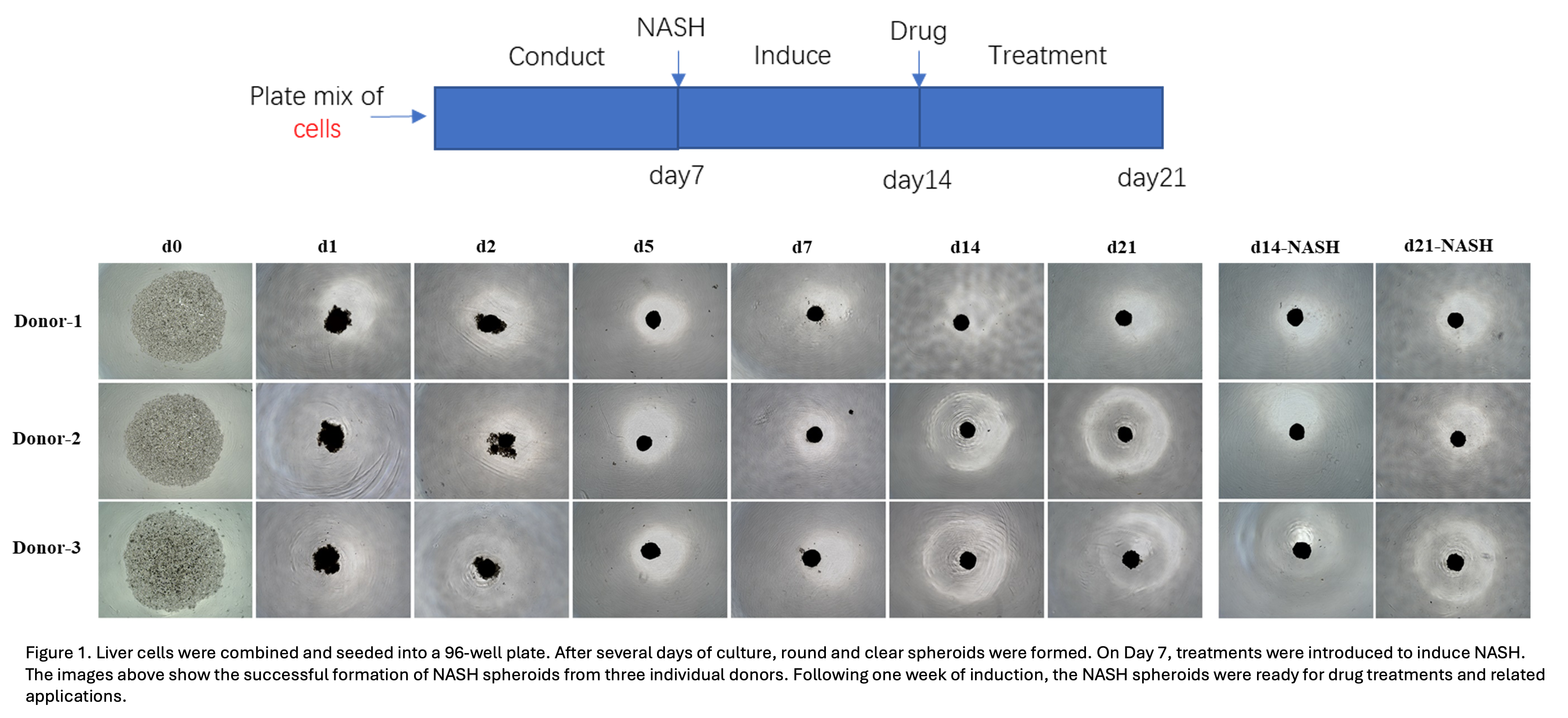
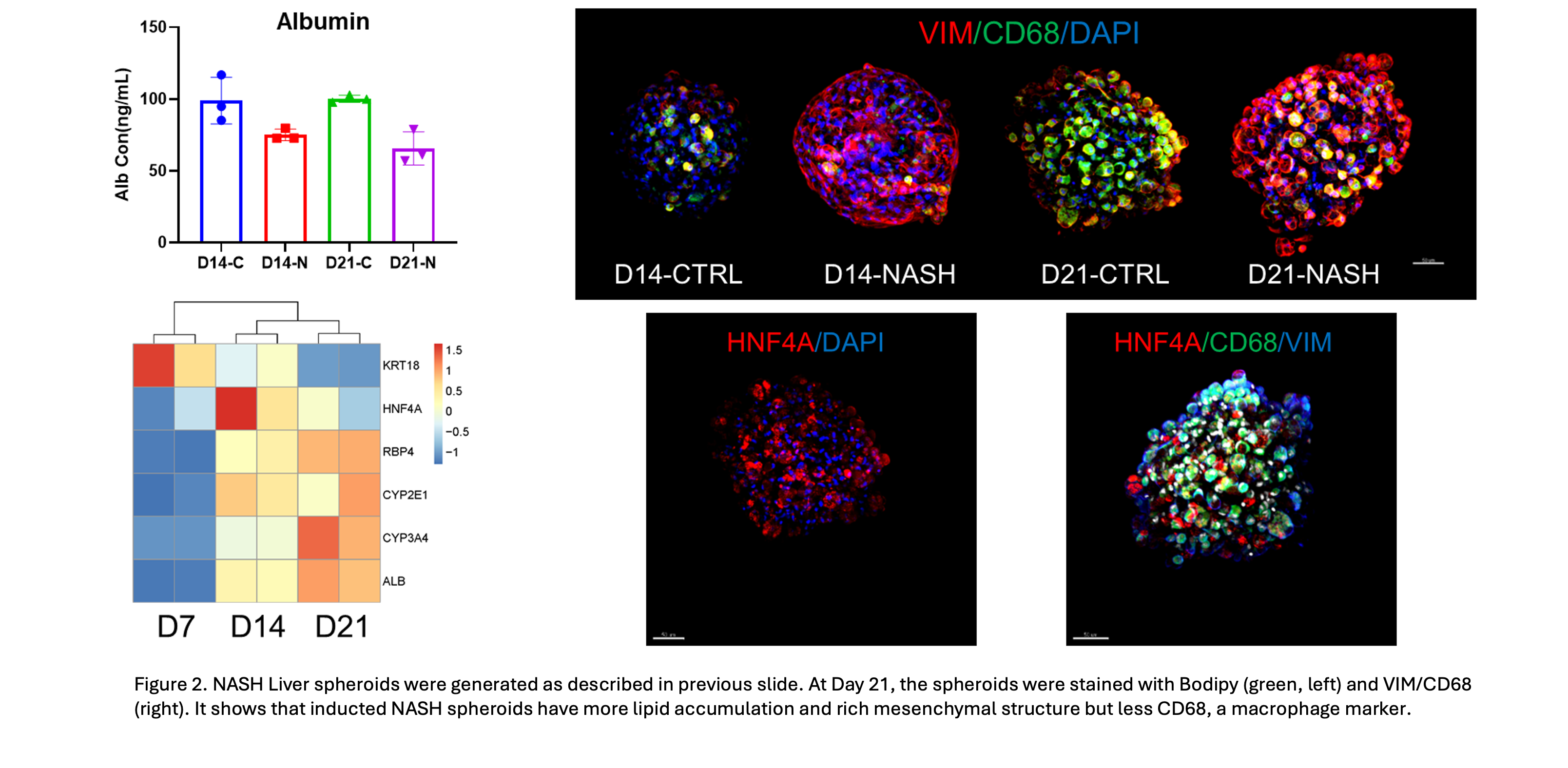
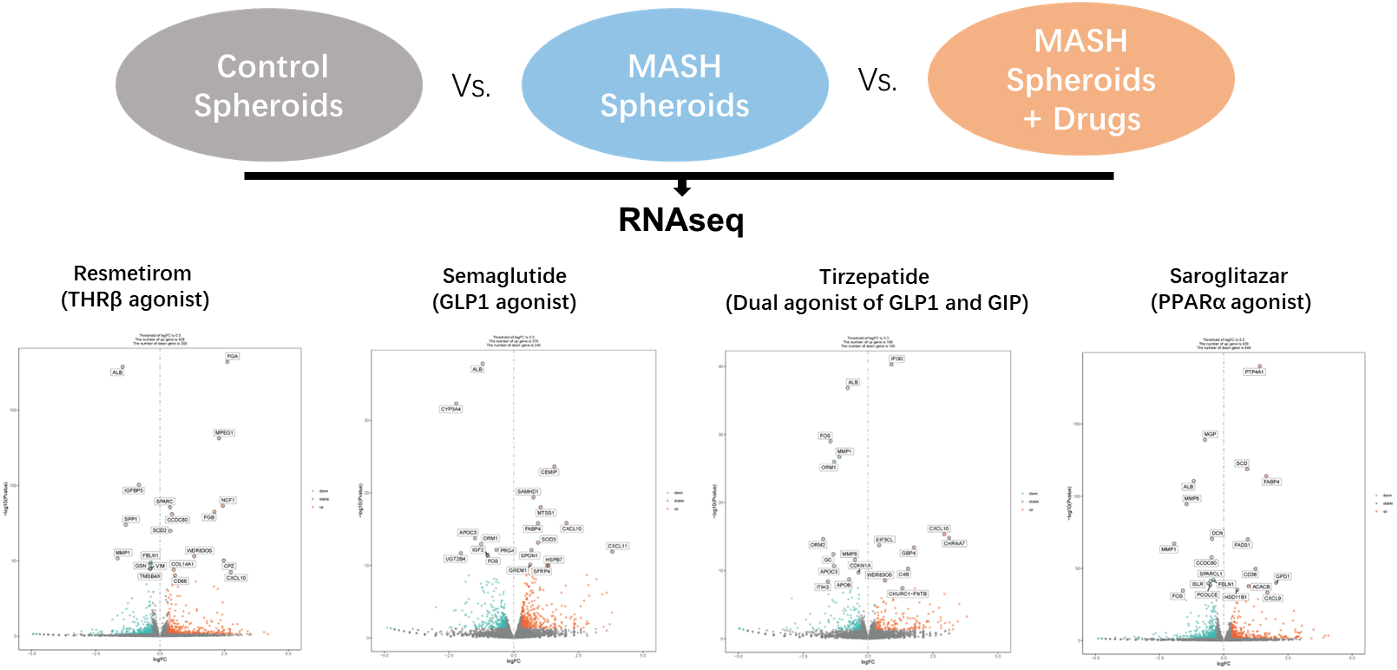
The 3D NASH (Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis) model developed by TriDix Bio is an advanced in-vitro liver culture system designed to replicate the complex microenvironment and pathophysiology of NASH. Unlike traditional 2D monolayer cultures, this model utilizes liver spheroids composed of multiple liver cell types, including primary hepatocytes, Kupffer cells, hepatic stellate cells, and liver sinusoidal endothelial cells, to closely mimic disease conditions. It provides a versatile platform for mechanistic studies of NASH onset and progression, as well as for drug screening and efficacy evaluation of anti-steatotic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-fibrotic compounds.
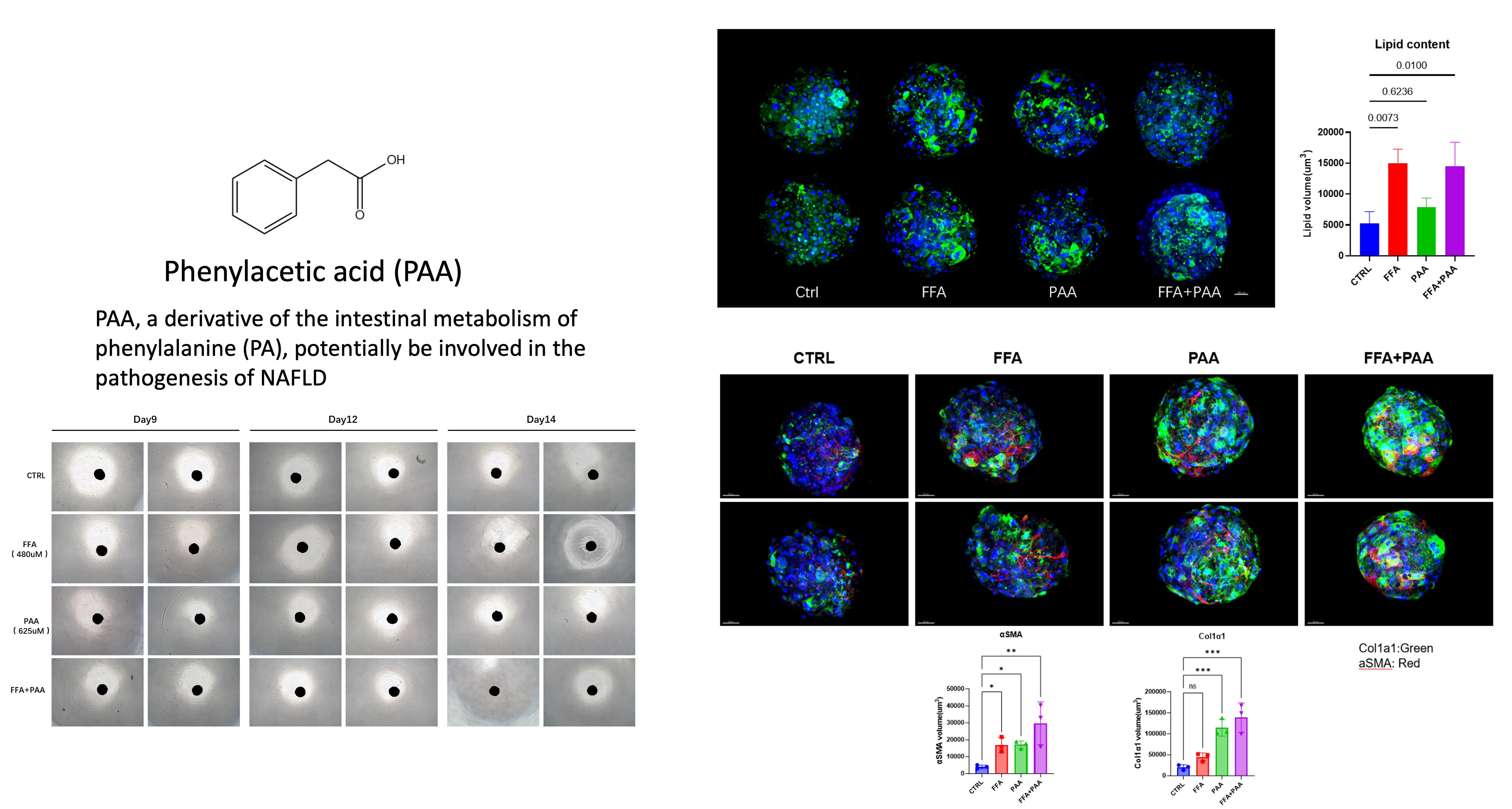
The 3D hepatic steatosis model developed by Tridix Bio is an advanced in-vitro culture system designed to replicate lipid accumulation in the liver, a hallmark of early-stage fatty liver disease. In contrast to conventional 2D cultures, this model utilizes liver spheroids or organoids composed of key hepatic cell types, including primary hepatocytes, Kupffer cells, and hepatic stellate cells, arranged in a three-dimensional architecture. This structure preserves native cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions, closely mimicking the liver's physiological microenvironment. The model serves as a robust platform for compound screening to evaluate anti-steatotic activity and facilitates the study of disease progression from simple steatosis to advanced liver disorders.
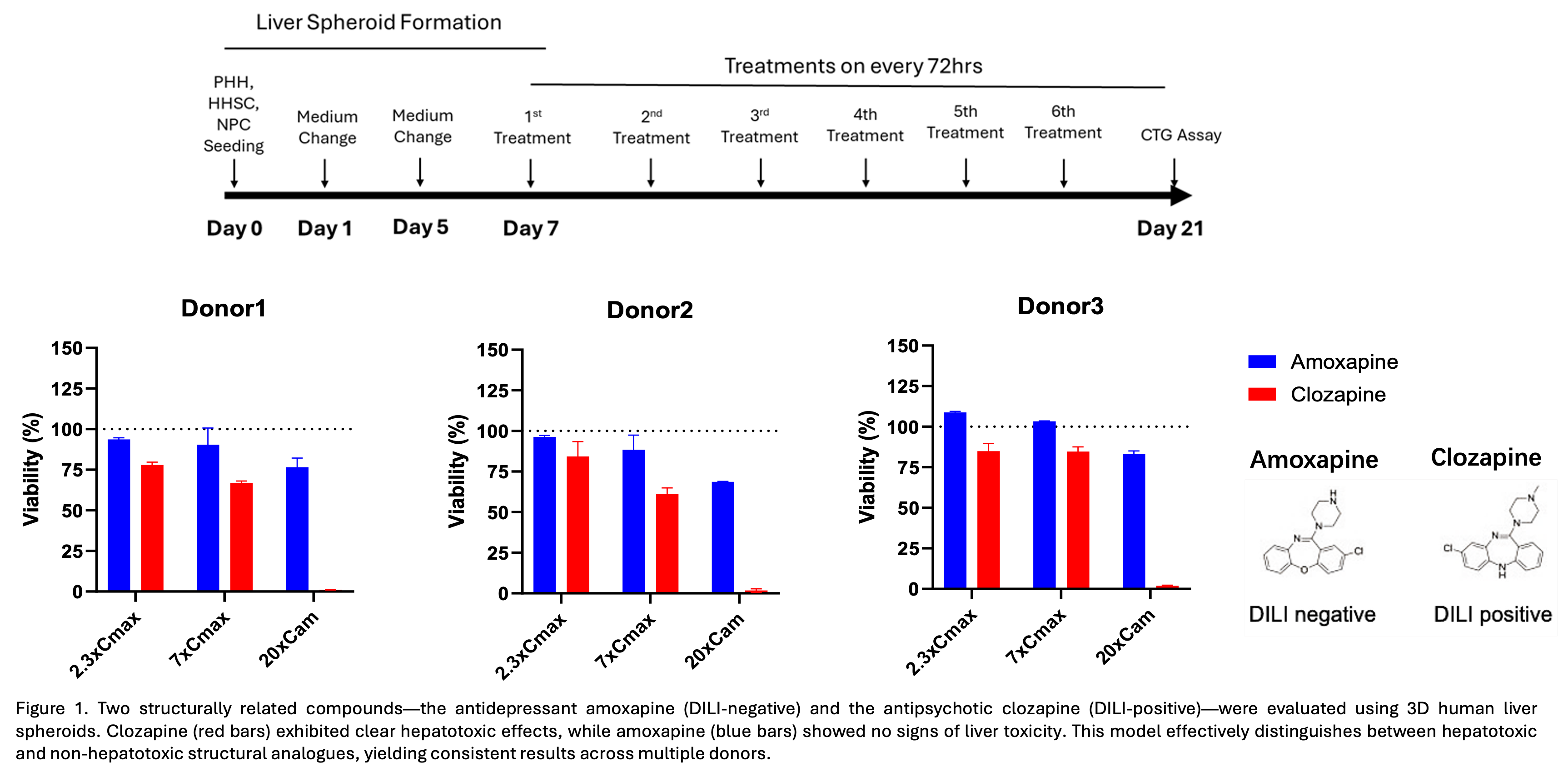
The 3D hepatotoxicity model developed by TriDixBio is an advanced in-vitro liver culture platform designed to evaluate the toxic effects of drugs, chemicals, and environmental agents on liver function and viability. Engineered with enhanced metabolic competence, a stable phenotype over extended culture periods, and superior predictability of in-vivo liver responses, this model provides a robust system for compound screening to assess hepatotoxic potential. It also enables mechanistic studies of drug-induced liver injury (DILI) and supports the evaluation of both acute and chronic toxicity.